Amiodarone Hydrochloride
Amiodarone Hydrochloride C25H29I2NO3.HCl: 681.77
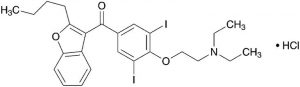
(2-Butylbenzofuran-3-yl){4-[2-(diethylamino)ethoxy]-3,5-diiodophenyl}methanone monohydrochloride [19774-82-4]
Amiodarone Hydrochloride, when dried, contains not less than 98.5%. and not more than 101.0% of amiodarone hydrochloride (C25H29I2NO3.HCl).
Description
Amiodarone Hydrochloride occurs as a white to pale yellowish white crystalline powder.
It is very soluble in water at 80oC, freely soluble in dichloromethane, soluble in methanol, sparingly soluble in ethanol (95), and very slightly soluble in water.
Melting point: about 161oC (with decomposition).
Identification
(1) Determine the absorption spectrum of a solution of Amiodarone Hydrochloride in ethanol (95) (1 in 100,000) as directed under Ultraviolet-visible Spectrophotometry <2.24>, and compare the spectrum with the Reference Spectrum: both spectra exhibit similar intensities of absorption at the same wavelengths.
(2) Determine the infrared absorption spectrum of Amiodarone Hydrochloride as directed in the potassium bromide disk method under Infrared Spectrophotometry <2.25>, and compare the spectrum with the Reference Spectrum: both spectra exhibit similar intensities of absorption at the same wave numbers.
(3) To 0.1 g of Amiodarone Hydrochloride add 10 mL of water, dissolve by warming at 80oC, and cool: the solution responds to the Qualitative Tests <1.09> (2) for chloride.
pH <2.54>
To 1.0 g of Amiodarone Hydrochloride add 20 mL of freshly boiled and cooled water,. dissolve by warming at 80oC, and cool: the pH of this solution is between 3.2 and 3.8.
Purity
(1) Clarity and color of solution—Dissolve 0.5 g of Amiodarone Hydrochloride in 10 mL of methanol: the solution is clear, and is not more colored than the following control solutions (1) and (2).
Control solution (1): To a mixture of 1.0 mL of Cobalt (II) Chloride CS, 2.4 mL of Iron (III) Chloride CS. and 0.4 mL of Copper (II) Sulfate CS, add diluted hydrochloric acid (1 in 40) to make 10.0 mL. To 2.5 mL of this solution add diluted hydrochloric acid (1 in 40) to make 20mL.
Control solution (2): To 3.0 mL of a mixture of 0.2 mL of Cobalt (II) Chloride CS, 9.6 mL of Iron (III) Chloride CS and 0.2 mL of Copper (II) Sulfate CS, add diluted hydrochloric acid (1 in 40) to make 100 mL.
(2) Iodine—To 1.50 g of Amiodarone Hydrochloride add 40 mL of water, dissolve by warming at 80oC, cool, add water to make exactly 50 mL, and use this solution as the sample stock solution.
Pipet 15 mL of this solution, add exactly 1 mL of 0.1 mol/L hydrochloric acid TS and exactly 1 mL of a solution of potassium iodate (107 in 10,000), add water to make exactly 20 mL, and use this solution as the sample solution. Separately, pipet 15 mL of the sample stock solution, add exactly 1 mL of 0.1 mol/L hydrochloric acid TS, exactly 1 mL of a solution of potassium iodide (441 in 5,000,000) and exactly 1 mL of a solution of potassium iodate (107 in 10,000), add water to make exactly 20 mL, and use this solution as the standard solution. Separately, pipet 15 mL of the sample stock solution, add exactly 1 mL of 0.1 mol/L hydrochloric acid TS, add water to make exactly 20 mL, and use this solution as the control solution.
Allow the sample solution, standard solution and control solution to stand in a dark place for 4 hours. Perform the test with the sample solution and standard solution as directed under Ultraviolet-visible Spectrophotometry <2.24>, using the control solution as the blank: the absorbance of the sample solution at 420 nm is not larger than 1/2 times the absorbance of the standard solution.
(3) Heavy metals <1.07>—Proceed with 1.0 g of Amiodarone Hydrochloride according to Method 4, and perform the test. Prepare the control solution with 2.0 mL of Standard Lead Solution (not more than 20 ppm).
(4) Related substance 1—Dissolve 0.5 g of Amiodarone Hydrochloride in 5 mL of dichloromethane, and use this solution as the sample solution.
Separately, dissolve 10 mg of 2-chloroethyl diethylamine hydrochloride in 50 mL of dichloromethane, and use this solution as the standard solution. Perform the test with these solutions as directed under Thin-layer Chromatography <2.03>. Spot 5 µL each of the sample solution and standard solution on a plate of silica gel with fluorescent indicator for thin-layer chromatography. Develop the plate with a mixture of dichloromethane, methanol and formic acid (17:2:1) to a distance of about 15 cm, and air-dry the plate. Spray evenly bismuth subnitrate TS and then hydrogen peroxide TS: the spot obtained from the sample solution corresponding to the spot from the standard solution is not more intense than the spot from the standard solution.
(5) Related substance 2—Dissolve 0.125 g of Amiodarone Hydrochloride in 25 mL of a mixture of water and acetonitrile for liquid chromatography (1:1), and use this solution as the sample solution.
Pipet 2 mL of the sample solution, and add a mixture of water and acetonitrile for liquid chromatography (1:1) to make exactly 50 mL. Pipet 1 mL of this solution, add a mixture of water and acetonitrile for liquid chromatography (1:1) to make exactly 20 mL, and use this solution as the standard solution. Perform the test with exactly 10 µL each of the sample solution and standard solution as directed under Liquid Chromatography <2.01> according to the following conditions. Determine each peak area by the automatic integration method: the area of the peak other than amiodarone obtained from the sample solution is not larger than the peak area of amiodarone obtained from the standard solution, and the total area of the peaks other than amiodarone from the sample solution is not larger than 2.5 times the peak area of amiodarone from the standard solution.
Operating conditions—
Detector: An ultraviolet absorption photometer (wavelength: 240 nm).
Column: A stainless steel column 4.6 mm in inside diameter and 15 cm in length,. packed with octadecylsilanized silica gel for liquid chromatography (5 µm in particle diameter).
Column temperature: A constant temperature of about 30oC.
Mobile phase: To 800 mL of water add 3.0 mL of acetic acid (100),. adjust the pH to 4.95 with ammonia solution (28), and add water to make 1000 mL. To 300 mL of this solution add 400 mL of acetonitrile for liquid chromatography and 300 mL of methanol for liquid chromatography.
Flow rate: Adjust so that the retention time of amiodarone is about 24 minutes.
Time span of measurement: About 2 times as long as the retention time of amiodarone.
System suitability—
Test for required detectability: Pipet 5 mL of the standard solution,. and add a mixture of water and acetonitrile for liquid chromatography (1:1) to make exactly 25 mL. Confirm that the peak area of amiodarone obtained from 10 µL of this solution is equivalent to 14 to 26% of that obtained from 10 µL of the standard solution.
System performance: When the procedure is run with 10 µL of the standard solution under the above operating conditions,. the number of theoretical plates and the symmetry factor of the peak of amiodarone are not less than 5000 and not more than 1.5, respectively.
System repeatability: When the test is repeated 6 times with 10 µL of the standard solution under the above operating conditions,. the relative standard deviation of the peak area of amiodarone is not more than 1.0%.
Loss on drying <2.41>
Not more than 0.5% (1 g, reduced pressure not exceeding 0.3 kPa, 50oC, 4 hours).
Residue on ignition <2.44>
Not more than 0.1% (1 g).
Assay
Weigh accurately about 0.6 g of Amiodarone Hydrochloride, previously dried,. dissolve in 40 mL of a mixture of acetic anhydride and acetic acid (100) (3:1), and titrate <2.50> with 0.1 mol/L perchloric acid VS (potentiometric titration). Perform a blank determination in the same manner, and make any necessary correction.
Each mL of 0.1 mol/L perchloric acid VS
= 68.18 mg of C25H29I2NO3.HCl
Containers and storage
Containers – Tight containers.
Storage – Light-resistant.
THE JAPANESE PHARMACOPOEIA
SEVENTEENTH EDITION
PLEASE TO REFER VNRAS.COM