Nifedipine
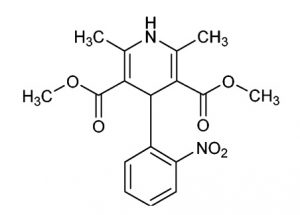
Nifedipine C17H18N2O6: 346.33
Dimethyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate [21829-25-4]
Nifedipine contains not less than 98.0% and not more than 102.0% of nifedipine (C17H18N2O6), calculated on the dried basis.
Description
Nifedipine occurs as a yellow crystalline powder. It is odorless and tasteless.
It is freely soluble in acetone and in dichloromethane, sparingly soluble in methanol, in ethanol (95) and in acetic acid (100), slightly soluble in diethyl ether, and practically insoluble in water.
It is affected by light.
Identification
(1) Dissolve 0.05 g of Nifedipine in 5 mL of ethanol (95), and add 5 mL of hydrochloric acid and 2 g of zinc powder. Allow to stand for 5 minutes, and filter: the filtrate responds to the Qualitative Tests <1.09> for primary aromatic amines, developing a red-purple color.
(2) Determine the absorption spectrum of a solution of Nifedipine in methanol (1 in 100,000) as directed under Ultraviolet-visible Spectrophotometry <2.24>, and compare the spectrum with the Reference Spectrum: both spectra exhibitsimilar intensities of absorption at the same wavelengths.
(3) Determine the infrared absorption spectrum of Nifedipine, previously dried, as directed in the potassium bromide disk method under Infrared Spectrophotometry <2.25>, and compare the spectrum with the Reference Spectrum: both spectra exhibit similar intensities of absorption at the same wave numbers.
Melting point <2.60>
172 – 175oC
Purity
(1) Clarity and color of solution—Dissolve 0.5 g of Nifedipine in 5 mL of acetone: the solution is clear and yellow.
(2) Chloride <1.03>—To 2.5 g of Nifedipine add 12 mL of dilute acetic acid and 13 mL of water, and heat to boil. After cooling, filter, and discard the first 10 mL of the filtrate. To 5 mL of the subsequent filtrate add 6 mL of dilute nitric acid and water to make 50 mL, and perform the test using this solution as the test solution. Prepare the control solution with 0.30 mL of 0.01 mol/L hydrochloric acid VS (not more than 0.021%).
(3) Sulfate <1.14>—To 4 mL of the filtrate obtained in (2) add 1 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid and water to make 50 mL. Perform the test using this solution as the test solution. Prepare the control solution with 0.45 mL of 0.005 mol/L sulfuric acid VS (not more than 0.054%).
(4) Heavy metals <1.07>—Proceed with 2.0 g of Nifedipine according to Method 2, and perform the test. Prepare the control solution with 2.0 mL of Standard Lead Solution (not more than 10 ppm).
(5) Arsenic <1.11>— Prepare the test solution with 1.0 g of Nifedipine according to Method 3, and perform the test (not more than 2 ppm).
(6) Basic substances—The procedure should be performed under protection from light in light-resistant vessels. Dissolve 5.0 g of Nifedipine in 80 mL of a mixture of acetone and acetic acid (100) (5:3), and titrate <2.50> with 0.02 mol/L perchloric acid VS (potentiometric titration). Perform a blank determination, and make any necessary correction.
Not more than 1.9 mL of 0.02 mol/L perchloric acid VS is consumed.
(7) Dimethyl-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrosophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate—The procedure should be performed under protection from light in light-resistant vessels. Dissolve 0.15 g of Nifedipine in dichloromethane to make exactly 10 mL, and use this solution as the sample solution.
Separately, dissolve 10 mg of dimethyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrosophenyl)-3,5-pyridine dicarboxylate for thin-layer chromatography in exactly 10 mL of dichloromethane.
Measure exactly 1 mL of this solution, add dichloromethane to make exactly 20 mL, and use this solution as the standard solution. Perform the test with these solutions as directed under Thin-layer Chromatography <2.03>. Spot 10 µL each of the sample solution and standard solution on a plate of silicagel with fluorescent indicator for thin-layer chromatography. Develop the plate with a mixture of cyclohexane and ethyl acetate (3:2) to a distance of about 10 cm, and air-dry the plate. Examine under ultraviolet light (main wavelength: 254 nm): the spot from the sample solution, corresponding to that from the standard solution, is not more intense than the spot from the standard solution.
Loss on drying <2.41>
Not more than 0.5% (0.5 g, 105oC, 2 hours).
Residue on ignition <2.44>
Not more than 0.1% (1 g).
Assay
The procedure should be performed under protection from light in light-resistant vessels. Weigh accurately about 0.12 g of Nifedipine, and dissolve in methanol to make exactly 200 mL. Measure exactly 5 mL of this solution, and add methanol to make exactly 100 mL. Determine the absorbance A of this solution at the wavelength of maximum absorption at about 350 nm as directed under Ultravioletvisible Spectrophotometry <2.24>.
Amount (mg) of nifedipine (C17H18N2O6)
= A/142.3 × 40,000
Containers and storage
Containers – Tight containers. Storage – Light-resistant.
THE JAPANESE PHARMACOPOEIA
SEVENTEENTH EDITION
PLEASE TO REFER VNRAS.COM